Inventory Accuracy Best Practices
Built For

Inventory Accuracy Best Practices

In the bustling business world, keeping tabs on your inventory can feel like a never-ending game of hide-and-seek. Yet, maintaining accurate inventory records is crucial for smooth operations and happy customers. Imagine promising a customer that their order is on its way, only to find out that the item is missing. Not a great scenario, right?
Inventory accuracy isn’t just about knowing what you have in stock—it’s about ensuring that every item is accounted for, right where it should be, and ready for action when needed. Accurate inventory data helps prevent overstocking or understocking, lowers holding costs, and enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and reliable order fulfillment.
In this article, we’ll explore the ins and outs of inventory accuracy and share some best practices to help you keep your inventory in check. From leveraging technology like barcode scanning and inventory management software to implementing regular cycle counts and audits, these strategies will help you boost accuracy and streamline your operations.
Understanding Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy might sound straightforward, but it’s the backbone of efficient business operations. At its core, inventory accuracy means that the physical count of items in your warehouse matches the records in your inventory management system. When these two figures align, you’re in good shape. When they don’t, you can run into a host of problems, from overselling products to losing track of stock.
Definition of Inventory Accuracy
Inventory accuracy is the percentage that reflects the alignment between recorded inventory levels and actual physical inventory. If your system says you have 100 units of a product and you count 100 units on the shelf, your accuracy for that product is 100%. It’s a simple concept, but consistently achieving high accuracy can be challenging.
Key Metrics for Measuring Inventory Accuracy
To keep your inventory accuracy in check, you need to regularly measure and monitor it. Here are some key metrics that can help:
Inventory Accuracy Rate: This is calculated by comparing the physical inventory count to the recorded count. The formula is:
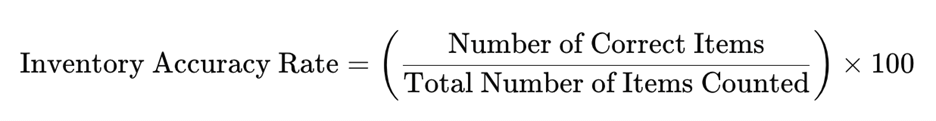
Cycle Count Accuracy: This metric involves regularly counting a subset of inventory to ensure accuracy over time. The results of these counts help identify discrepancies and understand their root causes.
Shrinkage Rate: This measures inventory loss due to theft, damage, or administrative errors. It’s calculated as:

Perfect Order Rate: This metric assesses the percentage of error-free orders, meaning the correct items were picked, packed, and delivered. A higher perfect order rate indicates better inventory accuracy.
Understanding these metrics and closely monitoring them helps identify issues early and take corrective actions. Regularly measuring your inventory accuracy ensures that your records are reliable, your operations run smoothly, and your customers stay happy.
Common Challenges in Maintaining Inventory Accuracy
Maintaining accurate inventory is no small feat. Even with the best systems, various challenges can throw off your numbers and disrupt your operations. Understanding these common challenges is the first step in addressing and overcoming them.
Human Errors in Data Entry and Counting
One of the most common culprits of inventory inaccuracies is human error. Manual data entry and counting processes are prone to mistakes. Employees might miscount items, enter incorrect quantities into the system, or even misplace inventory. Minor errors can add up over time, leading to significant discrepancies.
Inaccurate Inventory Tracking Systems
Using outdated or inadequate inventory tracking systems can also contribute to inaccuracies. Systems that rely heavily on manual updates, such as pen-and-paper tracking or spreadsheets, lack real-time tracking capabilities and often fail to provide an accurate picture of current stock levels. Without robust and reliable tracking systems, it’s easy for inventory records to become outdated or incorrect.
Misplaced or Lost Items
Items can easily be misplaced or lost in a busy warehouse. Poor organization, lack of labeling, and inefficient storage practices can lead to products being stored in the wrong locations or disappearing altogether. This affects inventory accuracy and slows down the picking and packing process.
Lack of Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular reviews and audits are essential for maintaining inventory accuracy, but they often get overlooked. Without routine checks, discrepancies can go unnoticed for extended periods, making pinpointing and addressing the root causes harder. Regular cycle counts and full inventory audits are critical practices for identifying and correcting errors before they escalate.
Changes in Demand and Stock Levels
Fluctuations in demand and changes in stock levels can also pose challenges. Sudden spikes in orders or unexpected supply chain disruptions can lead to inventory imbalances. Inventory management processes must be agile to adapt to these changes, or inaccuracies may occur.
Inefficient Warehouse Layout and Organization
An inefficient warehouse layout can make finding and counting items difficult. Cluttered aisles, poorly labeled shelves, and disorganized storage areas all contribute to inventory inaccuracies. A well-organized warehouse with clearly marked zones and easy-to-access inventory can significantly improve accuracy.
Theft and Shrinkage
Unfortunately, theft and shrinkage are realities that many businesses face. Shrinkage can lead to significant inventory losses, whether due to internal theft by employees or external theft by outsiders. Implementing security measures and monitoring systems can help mitigate this challenge.
By recognizing and understanding these common challenges, businesses can proactively address them. Implementing best practices, leveraging technology, and fostering a culture of accuracy and accountability are critical strategies for overcoming these obstacles and maintaining accurate inventory records.
Best Practices for Improving Inventory Accuracy

Achieving and maintaining high inventory accuracy requires a combination of strategic practices, advanced technology, and consistent effort. Here are some best practices to help you keep your inventory records precise and reliable.
Utilizing Inventory Management Software
Inventory management software with real-time tracking and integration with other business systems like QuickBooks, eCommerce platforms, and EDI systems can significantly enhance accuracy. Other key inventory software features include:
- Reorder Point Alerts trigger notifications when inventory levels fall below a predefined threshold and help prevent overstock and stockout situations, which can lead to inventory inaccuracies. By maintaining optimal stock levels, you reduce the chances of discrepancies.
- Centralized Inventory and Order Management allows you to manage all your inventory and orders from a single platform. It ensures that all data is synchronized and up-to-date across different sales channels and locations, helping to reduce errors that occur due to manual updates and disparate systems.
- Customizable Dashboards provide a real-time view of your inventory levels, order status, and key metrics. Customizable dashboards allow users to monitor critical information and quickly identify discrepancies or issues.
- Reporting and Analytic Tools help you analyze trends, forecast demand, and identify areas for improvement. Detailed reports provide insights into stock levels, turnover rates, and other critical metrics, enabling you to make informed decisions.
Implementing Barcode Scanning
- Barcode Technology Benefits: Barcode scanning is one of the most effective methods of improving inventory accuracy. By using barcode scanners, you eliminate manual data entry errors, speed up the counting process, and ensure that every item is tracked accurately from receipt to shipment.
- Barcoding Reduces Errors and Improves Tracking: Barcodes provide a unique identifier for each item, allowing for precise tracking throughout the supply chain. When scanned, barcodes instantly update inventory levels in your system, reducing the risk of discrepancies caused by human error.
Regular Cycle Counting
Cycle counting is an inventory method where a subset of inventory is counted regularly rather than performing a full inventory count all at once. This method helps to continuously monitor and maintain inventory accuracy.
How to Implement a Cycle Counting Program
- Develop a Schedule: Determine the frequency of counts based on item value and turnover rate.
- Assign Responsibilities: Ensure trained staff are responsible for counting and reconciling discrepancies.
- Analyze Results: Use the data from cycle counts to identify and address root causes of inaccuracies.
Employee Training and Accountability
- Importance of Training Staff: Properly trained employees are essential for maintaining inventory accuracy. Training should cover best practices for counting, data entry, and inventory management systems.
- Establishing Clear Procedures and Accountability: Create clear, documented procedures for all inventory-related tasks. Hold employees accountable for following these procedures and accurately recording inventory movements. Regular training sessions and refreshers can help reinforce these practices.
Regular Audits and Reconciliation
Schedule regular audits to count all inventory items and compare them with system records to identify and correct discrepancies.
Steps for Reconciliation of Discrepancies
- Investigate Variances: Determine the reasons for discrepancies between physical counts and system records.
- Adjust Records: Update inventory records to reflect the actual counts.
- Implement Corrective Actions: Address the root causes of discrepancies to prevent future occurrences.
Optimizing Warehouse Layout and Organization
An optimized warehouse layout reduces the time spent searching for items and minimizes the chances of misplacing stock. Efficient organization supports accurate counts and smooth operations. Strategies for efficient warehouse organization include:
- Clear Labeling: Use clear, consistent labeling for all storage areas and items.
- Logical Layout: Arrange items logically based on factors like picking frequency and product size.
- Clean and Orderly: Maintain a clean and organized warehouse to facilitate easy access and accurate counting.
Implementing best practices can significantly improve your inventory accuracy. Consistent application of these strategies and the right technology and training will help you maintain precise inventory records and streamline your business operations.
Call us at 817-870-1311