What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?
Built For

- Meaning of EOQ
- Basic formula to calculate EOQ
- Key components of EOQ
- Benefits contributed to calculating EOQ
- Role of inventory software in figuring EOQ
- Limitations and considerations of EOQ
What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?

Imagine you’re playing one of those strategy video games where you must keep your resources balanced—too much of one thing, and you’re wasting valuable space; too little, and you risk running out when the enemy attacks. Now, replace the game with real life, the resources with your business’s inventory, and the enemy with market demand. Welcome to the world of inventory management—a delicate dance of supply and demand. That’s where Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) steps into the spotlight.
You’ve probably heard of Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) or seen articles about the concept floating around online. EOQ isn’t just a fancy acronym to toss around in meetings; it can be a valuable tool to help hold down the fort in your storage room without breaking the bank. The concept of the equation is to provide you with the number of widgets to order to keep your business humming along smoothly without tripping over boxes of excess stock or facing the panic of empty shelves. However, it has some limitations, and we’ll also address those.
Breaking Down EOQ
Have you ever wondered just how many boxes of your best-selling product you should order to keep up with customer demand without turning your backroom into a cardboard jungle? That’s where Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) comes into play.
What is EOQ?
At its core, EOQ is a formula, but don’t let that scare you off. Economic Order Quantity calculates the ideal order quantity that will minimize your inventory costs, including the costs associated with ordering and holding stock. In other words, Economic Order Quantity is your guide for finding that sweet spot where you can order just enough to meet demand without overdoing it.
Solving the Goldilocks Dilemma
EOQ tackles the Goldilocks dilemma of inventory: order too much, and you’re tying up cash in stock that sits around collecting dust. Order too little, and you’re constantly reordering, which can rack up costs and leave you at risk of running out of products. Economic Order Quantity helps you find that “just right” quantity where your costs are lowest.
The Basic EOQ Formula
The Economic Order Quantity formula might look a little something like this:
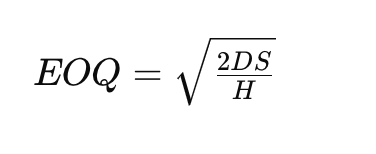
Where:
- 𝐷 stands for demand in units (typically over a year).
- 𝑆 is the cost of placing an order (per order).
- 𝐻 represents the holding cost (per unit, per year).
Think of it as a recipe that we will break down ingredient by ingredient to make the perfect economic order quantity cake.
The Ingredients of EOQ
If Economic Order Quantity were a recipe, what would you need in your pantry to prepare it? There are just three key ingredients: demand, ordering costs, and holding costs.
Demand: How Much Your Customers Want
Demand is the total number of units your customers will buy over a certain period, usually a year. This number can come from sales data, forecasts, or even some educated guesswork. Getting demand right is crucial; think of it as the foundation of your EOQ calculation.
Ordering Costs
Next up, ordering costs. We’re talking about everything from shipping fees to the labor involved in processing and receiving goods. It’s like paying for a ticket to see the show—necessary, but you don’t want it to cost more than the performance is worth.
Holding Costs: The Expense of Keeping Stock
Last but certainly not least, we have holding costs. This is the price of keeping inventory in stock, which includes storage, insurance, and the cost of money tied up in inventory. Think of holding costs as the rent you pay for the space your products take up while waiting to hit the road.
The Balancing Act
Understanding these three ingredients helps you balance your inventory act. Order too much, and your holding costs balloon up like a runaway hot air balloon. Order too little, and you’re placing orders so frequently that the ordering costs increase. Economic Order Quantity helps you find the balance to keep your business running smoothly.
The Benefits of Calculating EOQ
Now that we’ve got a handle on the key ingredients of EOQ let’s talk about why it’s worth your time to crunch these numbers. Here’s what you stand to gain:
Cost Savings
When you nail your EOQ, you’re trimming the fat off your inventory costs. By ordering the optimal amount of stock, you dodge unnecessary expenses from ordering too much or too little. It’s like having a personal finance guru for your inventory, helping you save those dollars where it counts.
Reduce Stockouts and Overstocks
With Economic Order Quantity, those dreaded stockouts and overstock scenarios become ghost stories from the past. You’re more likely to have just the right amount of stock at the right time. This means happy customers, fewer lost sales, and no more warehouse space wasted on unsold goods.
Smooth Operations
An optimized EOQ not only saves you money but also smoothens out the flow of your operations. Reordering inventory becomes a predictable, well-oiled process. This predictability means less stress for you and your team and more time to focus on other parts of your business.
Keep the Cash Flowing
When you’re not sinking unnecessary funds into excess inventory, your cash flow breathes a sigh of relief. Economic Order Quantity helps ensure that more of your capital is free to invest in growth opportunities rather than sitting idle on shelves or in a warehouse. It’s the financial flexibility every business owner dreams of.
Boost in Overall Efficiency
Lastly, EOQ can lead to a domino effect of efficiency across your business. From better use of storage space to improved labor allocation, getting your Economic Order Quantity right helps streamline various aspects of operations. This efficiency can lead to a leaner, more agile business ready to tackle new challenges.
Economic Order Quantity in Action
You’ve mixed the ingredients and understand the benefits, so what does EOQ look like out in the wild, in the day-to-day of your business? Let’s roll up our sleeves and see Economic Order Quantity in action, with a bit of help from our friend, inventory management software.
The Role of Inventory Management Software
Now, let’s add modern inventory management software into the mix. Instead of pulling out a calculator and crunching numbers, inventory software uses data-driven insights for precision accuracy, such as sales data and inventory levels, to assist you in computing the Economic Order Quantity.
Calculating EOQ: A Step-by-Step Example
Let’s say you own a business that sells specialty coffee beans. Here’s how you would calculate the EOQ:
- Annual demand (𝐷) for your coffee beans is 1,000 bags.
- The cost to place an order (𝑆), including shipping and handling, comes to $50 each time you order.
- The holding cost (𝐻), or the cost to store each bag of coffee beans for a year, is $5.
The EOQ formula is:
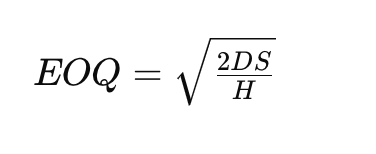
Plugging in the numbers:
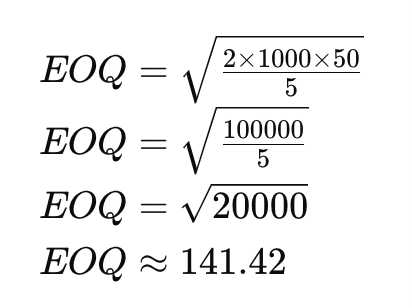
So, the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) for your coffee beans is approximately 141 bags. This means ordering 141 bags of coffee beans at a time is the most cost-effective strategy to minimize inventory costs.
Remember, EOQ is a starting point—it gives you an optimal number based on constant demand and costs, but real-world factors may require adjustments to this figure.
EOQ Limitations and Considerations

As we’ve seen, Economic Order Quantity can be a powerful tool in your inventory management arsenal. But it only solves some inventory challenges. Like any model based on assumptions, EOQ has limitations and considerations that must be factored into its application.
Fluctuating Demand
EOQ works beautifully in a vacuum where demand is steady and predictable. But what about seasonal spikes or unexpected trends? The Economic Order Quantity model assumes demand is constant, which can be a bit of a stretch in our fast-paced, ever-changing marketplaces. Businesses need to be nimble and adjust EOQ calculations to account for these variations in demand.
Lead Times
Another assumption EOQ makes is that lead times—the time between placing an order and receiving it—are consistent. In reality, suppliers can be unpredictable. Strikes, shortages, and shipping delays can all throw a wrench in the works, meaning you might need to hold more stock just in case.
One-Size Doesn’t Fit All
Economic Order Quantity provides a one-size-fits-all number, but every product might not fit into the same mold in the real world. High-value items with low turnover might need a different approach than low-cost, fast-moving goods. Applying EOQ across the board without considering the uniqueness of each product can lead to inefficiencies.
Storage Space
Storage space is another factor that EOQ doesn’t take into account. If your Economic Order Quantity calculation suggests you order 500 units, but your storage room can only fit 250, you’ve got a problem. Being aware of your physical constraints is vital before you give the green light on any EOQ-driven order.
EOQ and Technology
Inventory management software assists with Economic Order Quantity calculations, making applying them in real-life scenarios easier. However, even the most advanced software can’t fully compensate for EOQ’s limitations. It’s essential to use EOQ as a guideline rather than a strict rule and to remain flexible and adaptable in inventory management practices.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) FAQs
What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a formula used by businesses to determine the optimal number of units to order to minimize the costs associated with inventory, such as holding and ordering costs. It helps manage inventory more efficiently by ordering the right stock.
How do you calculate EOQ?
EOQ is calculated using a formula where:
·D represents the annual product demand.
·S is the per-order cost of placing an order.
·H is the holding or carrying cost per unit per year.
Why is EOQ important in inventory management?
EOQ helps businesses reduce costs related to inventory management. Companies can avoid excess inventory and shortages by calculating the ideal order quantity and improving cash flow and operational efficiency.
Can EOQ change over time?
EOQ can change over time as demand, order costs, and holding costs fluctuate. It’s essential for businesses to regularly review and adjust their EOQ to reflect current market conditions and internal changes.
Are there limitations to using EOQ?
EOQ has limitations. It assumes steady demand and lead times, which is not always the case in the real world. It also doesn’t consider constraints like storage capacity or varying product characteristics. Businesses should use EOQ as a guide rather than a strict rule.
Call us at 817-870-1311