Smart Inventory Management Strategies: A Practical Guide
Built For


Good inventory strategy protects cash, prevents stockouts, and keeps customers happy. Across top guides, the most reliable playbook blends classification (what matters most), replenishment rules (when and how much), and execution controls (how to keep it accurate)—increasingly powered by analytics.

1) ABC analysis (prioritize what moves the needle)
Classify SKUs by contribution to revenue or margin: A (vital few), B (moderate), C (many but low impact). Focus forecasting, cycle counts, and supplier attention on A-items first.
2) Demand forecasting (plan with data)
Use history, seasonality, promotions, and lead-time variability to project demand. Forecast quality improves reorder points and safety stock, and it’s a top lever to lower excess inventory.
3) Reorder point (ROP) planning
Set a trigger that tells you when to buy: average demand during lead time plus safety stock. Pair with alerts to avoid last-minute expedites.
4) Safety stock
Hold a calculated buffer for demand spikes or supplier slips. Right-sized buffers reduce lost sales without bloating carrying costs.
5) Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
A classic formula balances order cost and carrying cost to suggest an optimal lot size; still useful when demand is steady and costs are known.
6) Just-in-Time (JIT)
Reduce on-hand inventory by syncing purchases and production to real demand. Requires reliable suppliers and tight signals.
7) Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
Let suppliers replenish based on your consumption data under agreed service levels. Works well on fast-moving C-items or packaging materials.
8) Min-max policies
Define a “floor” (min) that triggers replenishment to a “ceiling” (max). Simple to operate and easy for teams to understand.
9) Perpetual inventory with cycle counting
Keep records live with barcode/mobile transactions and replace annual shutdowns with frequent cycle counts prioritized by ABC class. Reduces shrink and surprises.
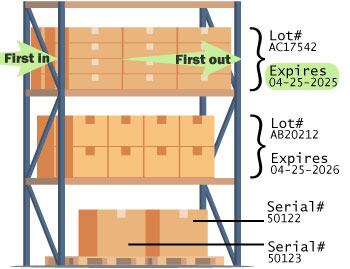
10) Lot/serial tracking and FIFO
Track traceability, expiry, or warranty by lot or serial. Issue oldest stock first (FIFO) to minimize spoilage and write-offs.
11) Multi-location and transfer planning
Balance stock across warehouses, stores, or channels. Use demand by region and transfer lead times to keep the right items nearest the customer.
12) Dropshipping and cross-docking
For selected SKUs, ship from suppliers to customers or move inbound directly to outbound. Lowers holding cost but needs strong order routing and visibility.
13) Returns and reverse logistics
Standardize inspection, disposition, and putaway of returns. Clean processes recover value and keep records accurate.
14) Service-level driven planning
Choose target fill rates by item class and compute buffers accordingly. Aligns inventory dollars with customer promises.
15) Promotions and new product planning
Isolate promo lift from baseline, and ramp new SKUs using look-alike demand until you have real history. Prevents panic buying and excess.

16) Lead-time management
Measure actual supplier lead times and variability. Reducing variability is often more valuable than shaving a day or two off averages.
17) Procurement optimization
Bundle orders, schedule standing POs, and negotiate MOQs based on real demand, not guesswork. Tie buys to forecasts and service goals.
18) KPI-driven continuous improvement
Track turnover, DIO, fill rate, backorder rate, GMROI, and accuracy. Use dashboards to spot drift early and tune parameters. Leading sources call this a foundation of modern practice.
19) Technology integration
Guides consistently stress connecting inventory with accounting, ecommerce, POS, and WMS so data flows cleanly and decisions reflect reality.
How to choose the right inventory management strategy
Most teams combine a few core tactics—ABC, forecasting, ROP/safety stock, and perpetual inventory—with selective use of EOQ, JIT, VMI, and multi-location balancing. As you grow, lean on KPIs and scenario planning to refine buffers, order sizes, and service targets. That blend mirrors what the highest-ranking playbooks recommend today.
A quick checklist to implement, step by step
- Classify SKUs (ABC) and set service targets.
- Clean master data and enable perpetual transactions.
- Build a baseline forecast and measure error.
- Calculate ROP and safety stock by item-location.
- Pick a replenishment policy: EOQ or min-max.
- Instrument KPIs and review monthly.
- Add advanced analytics where volatility or complexity is highest.
How Acctivate makes inventory management easy
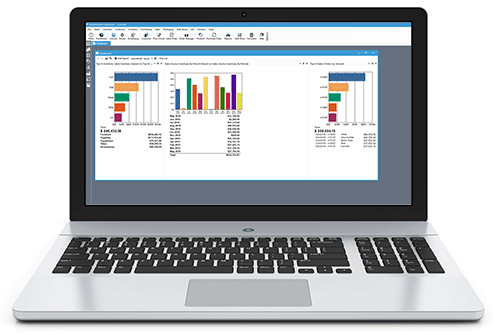
If you are ready to put these strategies to work without duct-taping spreadsheets, Acctivate inventory management software brings them together in one place: real-time, multi-location control; barcode-driven perpetual inventory and cycle counts; ABC reporting, forecasting, reorder points, safety stock, and min-max; lot/serial traceability and FIFO; KPI dashboards for turnover, DIO, fill rate, backorders, GMROI, and accuracy; and native QuickBooks integration so operations and accounting stay in sync. When you want to see it in action, watch a demo overview of Acctivate, and connect with us to walk through your use cases end to end.
Call us at 817-870-1311




